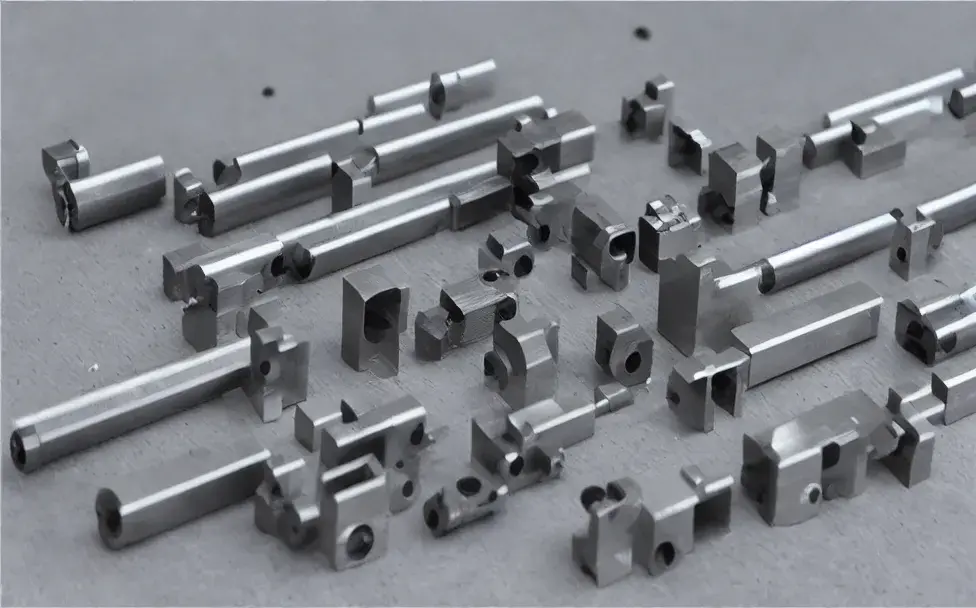
Understanding Turning and Milling Stock
Turning and milling stock refers to the process of shaping raw materials into the desired shape and size through the use of specialized machinery and cutting tools. This process is used in various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, to manufacture precise and intricate parts.
The Importance of Precision
In today’s world, precision is of utmost importance in almost every industry. Whether it’s the production of aircraft components or medical devices, precision is essential to ensure the safety and quality of the end product. Turning and milling stock plays a crucial role in achieving this precision, as it allows manufacturers to create parts with exact dimensions, smooth surfaces, and consistent tolerances.
The Benefits of Turning and Milling Stock
Using turning and milling stock can greatly benefit manufacturers in several ways. Firstly, it saves time and reduces waste as the process is faster and more efficient compared to traditional machining methods. Secondly, it provides greater accuracy and consistency, as the process is controlled by computers, which eliminates the possibility of human error. Lastly, it enables the creation of complex geometries, as the process can accommodate a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
The Different Types of Turning and Milling Stock

There are several different types of turning and milling stock, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types include:
Round bar stock: This type of stock is commonly used for manufacturing shafts, spindles, and gears.
Square and rectangular bar stock: This type of stock is commonly used for creating blocks, fixtures, and brackets.
Hexagonal bar stock: This type of stock is used for manufacturing nuts, bolts, and other fasteners.
Plate stock: This type of stock is used for creating flat components, such as flanges and covers.
Milling and Turning – Similarities:
Both turning and milling are machining processes that use cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece.
Both processes can produce highly accurate parts and components.
Both turning and milling can be performed on a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Differences:
Shape Capabilities: Turning is limited to cylindrical parts, while milling can produce a wide range of shapes and forms.
Speed: Turning is generally faster than milling, especially for large production runs.
Surface Finish: Milling typically results in a smoother surface finish
The Future of Turning and Milling Stock
As technology continues to advance, the field of turning and milling stock is poised for even greater growth and innovation. With the use of 3D printing, manufacturers can now create parts with even greater precision and complexity, while reducing the time and cost involved in the production process. Additionally, the use of advanced materials, such as titanium and carbon fiber, has made it possible to create lighter, stronger, and more durabe parts.
In conclusion, turning and milling stock is a vital aspect of precision manufacturing, and its importance will only continue to grow in the future. Whether you’re a manufacturer, designer, or engineer, understanding the basics of turning and milling stock will give you a competitive edge and enable you to create parts that meet the highest standards of quality and accuracy.