Content Navigator
- What is the Gear Hobbing Tool?
- Types of Gear Hobbing Tools
- Characteristics of Gear Hobbing Tools
- How to Choose Hobbing Tools?
What is the Gear Hobbing Tool?
The gear hob is a tool for processing straight and helical cylindrical gears according to the principle of helical gear meshing. It is equivalent to a helical gear with a small number of teeth and a large helix angle. Its appearance is worm-shaped.The gear hob is a tool for processing straight and helical cylindrical gears according to the principle of helical gear meshing. It is equivalent to a helical gear with a small number of teeth and a large helix angle. Its appearance is worm-shaped. According to the processing nature, it can be divided into fine cutting hob, rough cutting hob, shaving hob, scraping hob, extruding hob and grinding hob. According to the structure, it can be divided into integral hob, welding hob, Fabricated hobs and gear hobs.
Types of Gear Hobbing Tools
According to different structures, gear hobs can be divided into two types: integral hobs and insert hobs. According to the purpose, it can be divided into rough machining hob and finishing hob. According to the material cut by the hob, it can be divided into high-speed steel hob and carbide hob; according to the number of thread heads of the hob, it can be divided into single-head hob and hob. Multi head hob. In addition, according to the characteristics of the workpiece to be processed, various improvements can be made to the structure of the gear hob and the geometry of the hob tooth profile. Typical examples include small pressure angle hobs, wave-shaped edge hobs, unequal tooth High-speed hobs, full-cut hobs, etc., as well as front-shaving hobs, front-grinding hobs and front-shaving hobs. The cutter teeth of the latter two are relatively narrow, so that after hobbing to the depth, the tooth thickness of the workpiece still has a margin for grinding or shaving.
1.Integral high-speed steel gear hob.
Both the medium and small module hobs are made into an integral structure, as shown in Figure 6-3. There are two basic types of integral high-speed steel gears. Type I is suitable for 3A-grade hobs specified in JB/T3227-2013 “General Technical Conditions for High-precision Gear Hobs” and GB/T6084-2016 “General Technical Conditions for Gear Hobs” “Class 2A hobs as stipulated in “; Type II is suitable for hobs with four precisions of 2A, A, B and C as stipulated in GB/T6084-2016. The overall high-speed steel gear hob is made into a single head, right-handed, zero-degree rake angle, and straight groove.

2.Insert gear hob
The large modulus and medium modulus hobs can be made into an insert structure. On the one hand, it saves high-speed steel, and at the same time, it can ensure the heat treatment performance of the blade and increase the life of the hob. Due to the continuous improvement of forging and heat treatment processes, insert gear hobs with a modulus of more than 20mm are gradually replaced by integral high-speed steel gear hobs.
Insert gear hob:
Below is an insert gear hob with a modulus of 9-40 mm, which is made into a single-head, right-handed, zero-degree rake angle, straight groove form, and the accuracy grade is 2A, A , B, the tooth shape inspection should adopt the involute basic worm.

Positive rake angle insert gear hob:
Below is a positive rake angle insert gear hob with a modulus of 9 to 40mm, which is made into a single head, right-handed, and the rake angle at the top circle is 7°, For straight slots, involute basic worms should be used for tooth profile inspection.

3.Hob with cutting cone
When cutting helical gears with a large helix angle, the inclination angle of the hob axis is relatively large, and the projection length of the hob on different planes is shortened. The load distribution between the working cutter teeth is more even. When the helix angle of the processed gear is greater than 20°, a cutting cone should be processed at one end of the hob. The position of the cutting cone should be determined according to the helical direction of the gear to be cut, the helical direction of the hob and the feed direction when hobbing the gear.
4.Wave blade high efficiency rough cutting gear hob
During rough hobbing, the shape of the chip changes greatly, causing a large change in cutting force, causing vibration of the machine tool, and limiting the production efficiency of rough hobbing. After the hob tooth shape is relieved into a wave-shaped edge, the chip can be cut off, the shape of the chip changes little, the change of the cutting force is small, the vibration of the machine tool is small, and the cutting amount can be increased, and the effect is more significant when cutting hard-toothed gears. The wave depth is 0.8-1.2mm, and the wave pitch is 7-12mm. The corrugated and straight surfaces should be smoothly connected to avoid sharp corners.
- Full corrugated type, corrugated front and back staggered
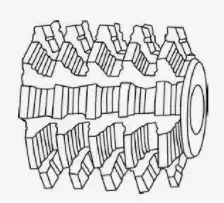
- The rows are corrugated, and the corrugations are not staggered

- With smooth tooth type, the corrugation does not stagger before and after

5.Clamping and bonding of large modulus gear hobs
Large modulus insert gear hob, the weight of the blade is heavy, and high-speed tool steel with large cross-section is required for forging, and the carbide segregation of high-speed tool steel raw materials increases with the increase of the cross-section, and the carbide segregation is high, not only the blade made of it The service life is low, and cracks are easy to appear during forging, heat treatment, grinding, and use, so the large modulus insert gear hob is expensive and the quality is not high. Machine clamping and bonding large modulus gear hobs overcome the above-mentioned shortcomings, changing a row of blades into one tooth and one blade, and can manufacture large modulus gear hobs with small cross-section high-speed tool steel.
6.Multi-head gear hob
The use of multi-head gear hobs can significantly improve the productivity of gear hobbing, especially when hobbing helical gears with a large number of teeth. The knife should be small, so the load on the side teeth of the hob will be reduced. Therefore, the multi-head hob with medium and small modulus is widely used in rough hobbing. The number of hob heads is usually 2 to 3 heads.
As the number of hob heads increases, the cutting load increases correspondingly, while the number of cuttings enveloping a tooth surface decreases proportionally. In order to improve the rigidity of the hob and reduce the edge of the cut gear surface, the outer diameter and aperture of the hob should be increased accordingly, and the number of circumferential teeth should also be increased. Also note:
- When the number of teeth z2 of the cut gear and the number of hob heads z1 are mutually prime numbers, the number of circumferential teeth zk of the hob and the number of heads z1 should also be mutually prime numbers. In this way, the manufacturing error of the hob will not be fully reflected on the gear when the gear is hobbed, which is beneficial to improving the precision of the gear.
- When the number of gear teeth z2 and the number of hob heads z1 have a common factor, the number of hob circumferential teeth zk should also be divisible by the number of hob heads z1, or have a common factor, because when the number of hob circumferential teeth cannot be divided by the hob When the number of heads is evenly divided, if one tooth is aligned with the center of the gear, then any tooth of the other heads cannot be aligned with the center of the gear, resulting in asymmetrical rolling out of the other teeth. Due to the small number of enveloping teeth of multi-head hob hobbing, the error caused by this asymmetry is often considerable. In this case, the multi-head hob is used for rough hobbing, and the hobbing allowance should be properly considered.
Characteristics of Gear Hobbing Tools
Below is a working principle diagram of machining gears with a gear hob. The hob axis is inclined at an angle ψ to the workpiece section. The rotary motion of the hob is the main motion. When machining spur gears, each time the hob turns, the workpiece turns over one tooth (when the hob is single-headed) or several teeth (when the hob is multi-headed), to form a generative motion, that is, circular feed motion . In order to cut the tooth profile on the full tooth width of the gear, the hob also needs to have a feed motion in the direction of the gear axis. When cutting helical gears, in addition to the above-mentioned movements, an additional rotation is required for the workpiece.

The hob is a relatively expensive metal cutting tool, which requires high thermal hardness and wear resistance, so the quenching temperature is relatively high, but slightly lower than that of the turning tool. Level 9.5 to 10. The first tempering should be treated with 350-380°C or secondary bainite treatment, and then high-temperature tempering at 550°C×1h for 3 times, overheating 1-2 grades, or even 3 grades, and the final tissue hardness can reach above 65HRC .
How to Choose Hobbing Tools?
The precision grades of gear hobs are divided into: 3A grade, 2A grade, A grade, B grade and C grade. When the gear tooth precision is at or above grade 6, it should be machined with a hob with 3A precision. The accuracy of pre-shaving, pre-grinding and pre-shaving hobs is generally A-level and B-level.
The key points for the selection of gear hobs are as follows:
- Choose according to the precision of the gear being machined. It is recommended to use integral hobs for gears with grade 7 precision and above, and blade hobs for others.
- Choose according to the hardness of the gear being processed. If the hardness of the tooth blank is >300HBW, it is recommended to use a blade hob.
- Choose according to gear batch and efficiency. If the batch is large and has high efficiency requirements, the blade hob is used.
I believe that through the above, you have a preliminary understanding of gear hobbing tools. Below we will introduce the quality testing tools of gear products: gear measuring instruments, meshing instrument, etc., so that you can further understand gear hobbing products. However, the quality assurance of gear hobbing products requires not only the best cutting tools but also a reliable manufacturer. I believe that Jinwang will be your most suitable partner.